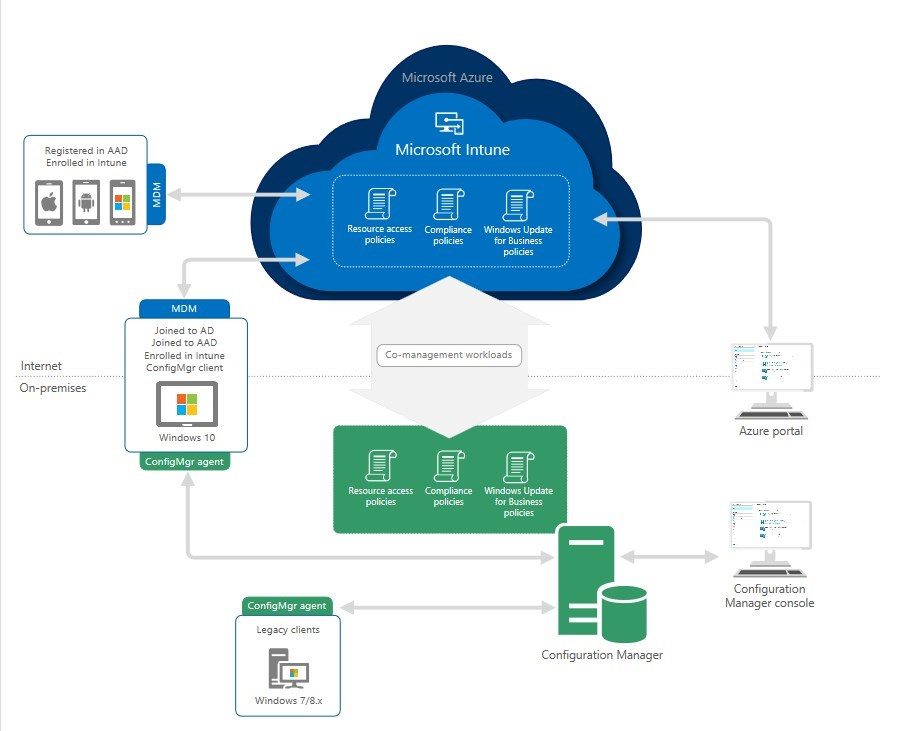

With the release of SCCM 1710, one of the key new features is the SCCM Co-Management possibility with Microsoft Intune. Co-management allows you to manage Windows 10 (and later) devices simultaneously with both SCCM and Microsoft Intune. This approach enhances your existing Configuration Manager setup by integrating new cloud capabilities. With co-management, you gain the flexibility to choose the workload of each tools to meet your organization’s needs.
Comanagement enables some interesting features like conditional access, remote actions with Intune, and provisioning using AutoPilot. This is great to slowly phase into Intune.
There are two main paths to reaching co-management:
- Windows 10 and later devices managed by Configuration Manager and hybrid EntraID joined get enrolled into Intune
- Windows 10 devices that are enrolled in Intune and then installed with the Configuration Manager client
We will describe how to enable co-management and enroll an SCCM-managed Windows 10 device into Intune.
SCCM Co-Management Prerequisites
- SCCM 1710 or later
- EntraID Subscription
- EMS or Intune license for all users
- Azure AD automatic enrollment enabled
- Following our blog post, only configure Azure AD. Do not follow instructions for Windows 10, those options have changed between 1703 and 1709.
- Intune subscription (MDM authority in Intune set to Intune)
- See our post to change the MDM authority from SCCM to Intune
- Windows 10 1709 or higher
- Client computer using Hybrid EntraID Joined (domain + AAD joined)
Concept of SCCM 1710 Co-Management
Microsoft provides a great diagram that explains how the workload is managed when co-management is activated.

The co-management provides the ability to offload some workload to Intune. There are 3 categories of workloads :
- Compliance policies
- Windows Update policies
- Resource access policies
- Endpoint Protection
- Device configuration
- Office Click-to-Run apps
- Client apps
Once a workload is offloaded to Intune, SCCM no longer manages those settings on the Windows client.
The co-management is designed to allow administrators to Pilot to specific computers before completely offloading a workload to Intune, allowing a smooth transition.
Enable SCCM 1710 Co-Management
Here’s how to enable SCCM co-management.
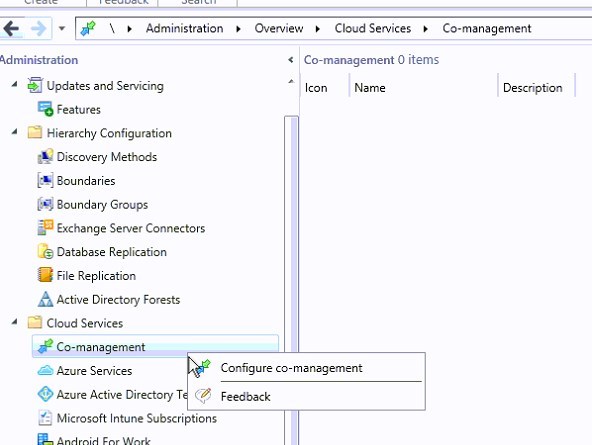
- Go to Administration / Cloud Services / Co-Management and select Configure Co-Management
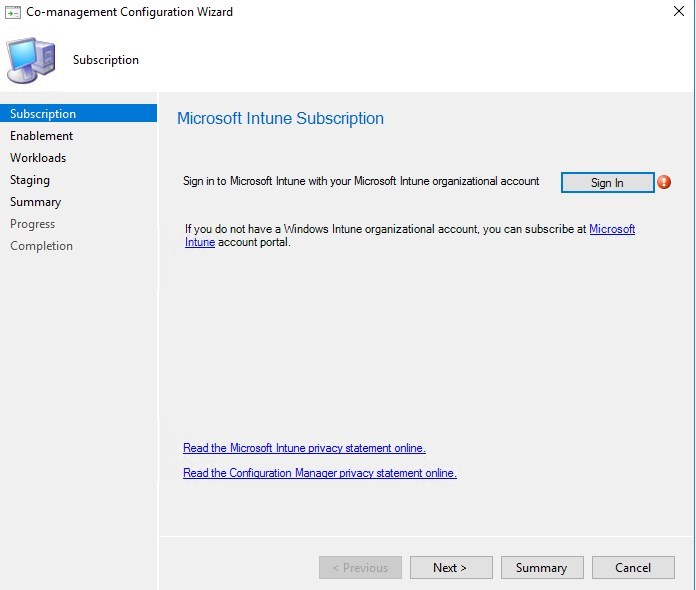
- Enter your Intune Credentials
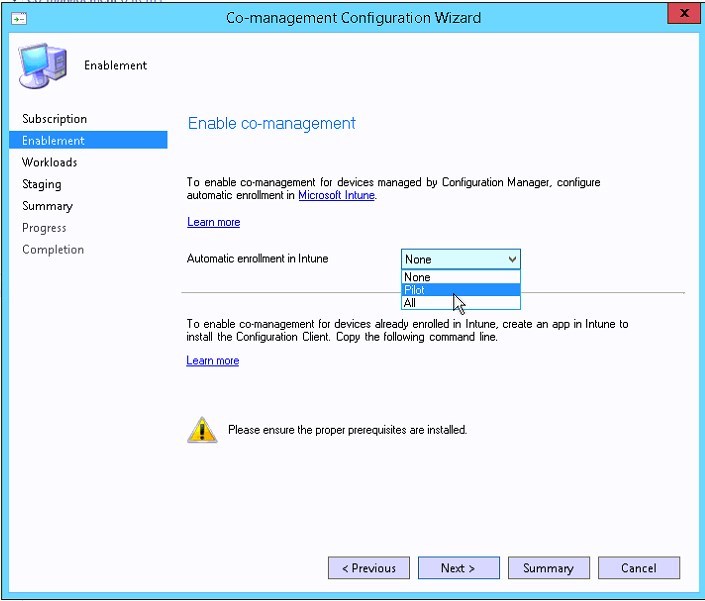
- Select who can Automatic Enroll in Intune
- We strongly recommend beginning with Pilot. This will require selecting a collection to limit allowed computers only
- This can be changed later when ready to production roll-out
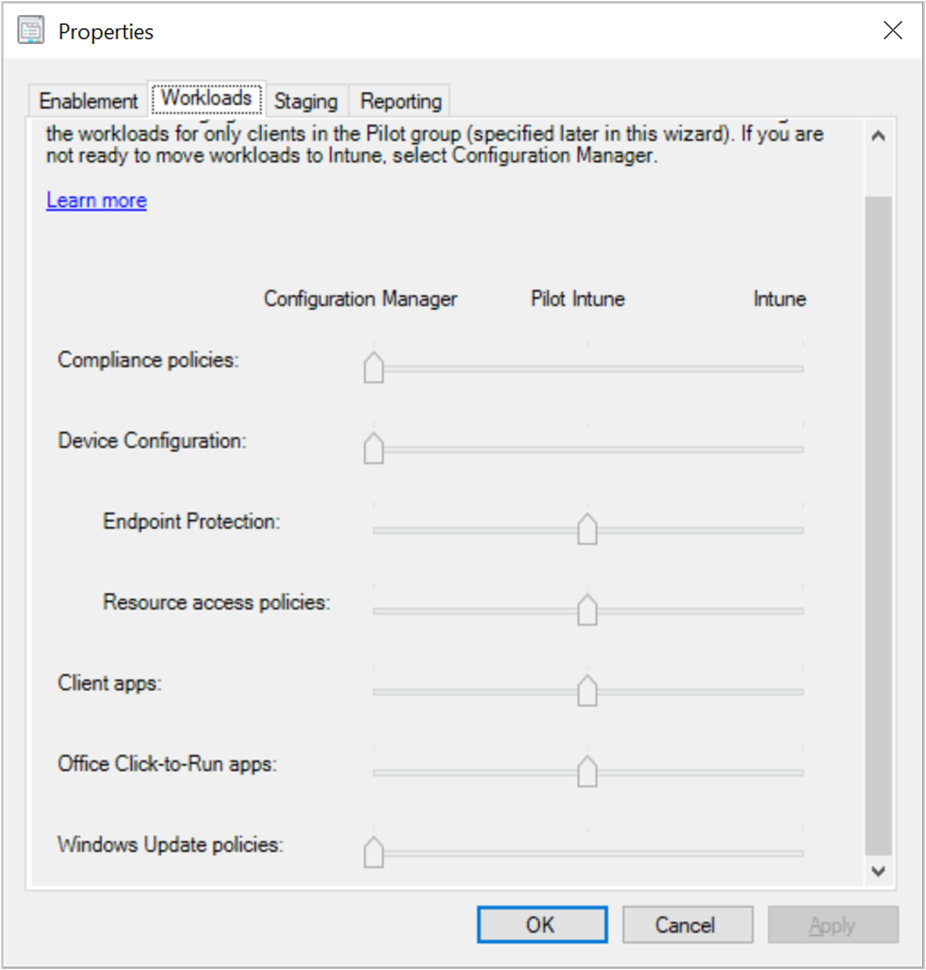
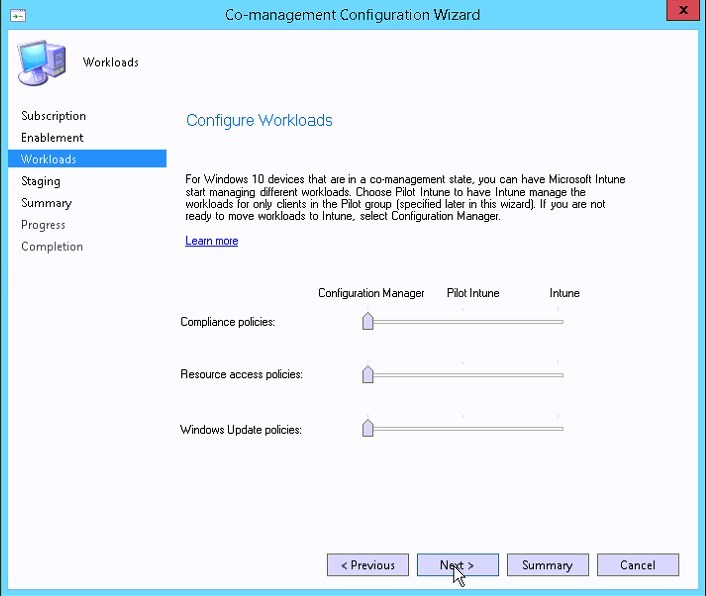
- Configure the Workloads
- This can be left to all SCCM for now and adjusted later on
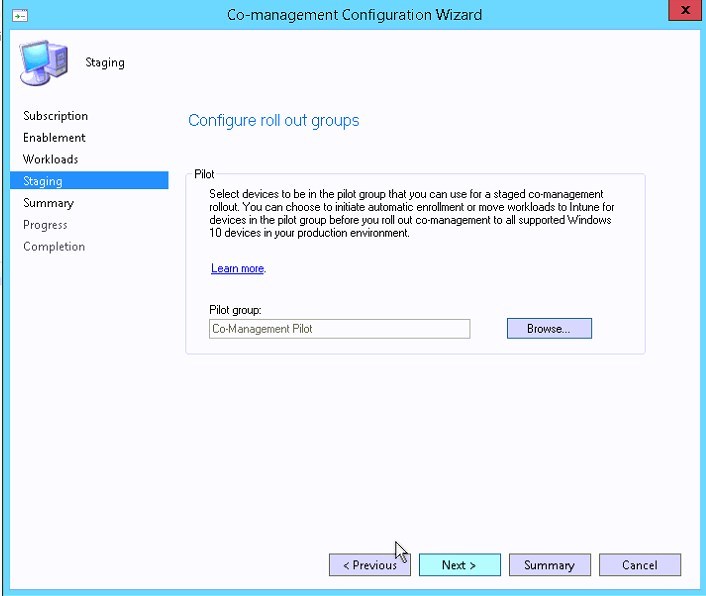
- Select a computer collection to be used for pilot
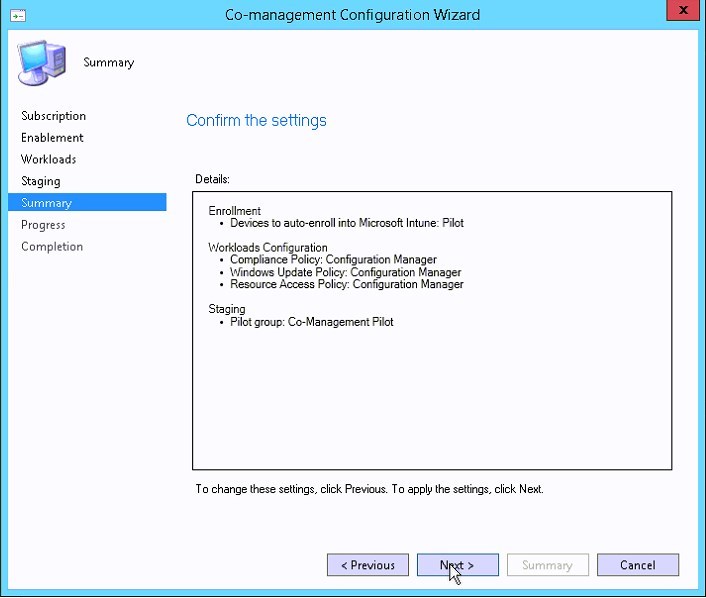
- Summary, click Next
- Co-Management is then enabled
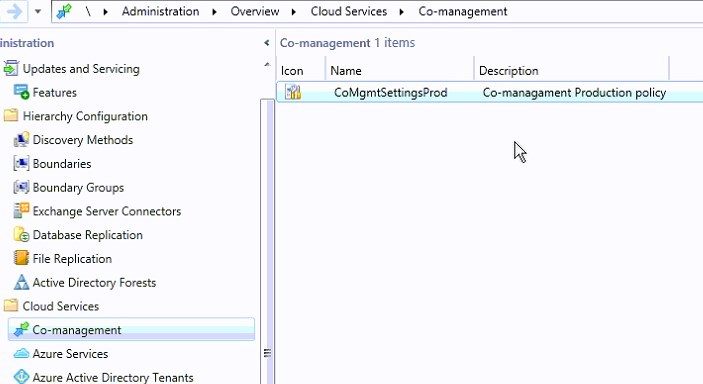
- Under Properties / Enablement, the Automatic enrollment can be changed from Pilot to Production
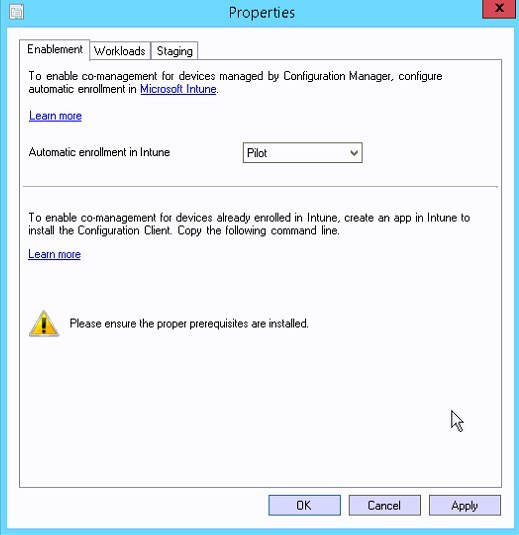
- Under Properties / Workloads, it’s possible to set the slider for the different workloads and assign them to Pilot or Intune
Before changing any workload to pilot, it’s time to enroll a computer into Intune, while still managed by SCCM.
Enroll Windows 10 1709 client into Intune for Co-management
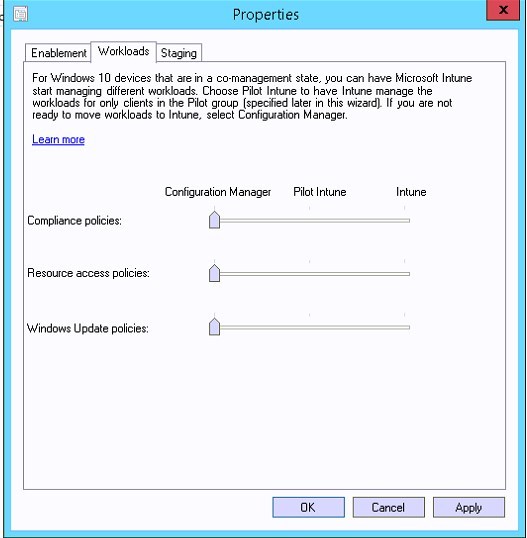
- The first step is to enable the GPO to enable Auto MDM Enrollment with AAD Token
- Location : Computer Configuration/Administrative Template/Windows Components/MDM
If you don’t see the GPO, your Central store needs to be updated with the latest ADMX from Windows 10 1709
- Next, add the computer to the Pilot collection for Co-Management
- After the next machine policy update, the client will begin to enroll.
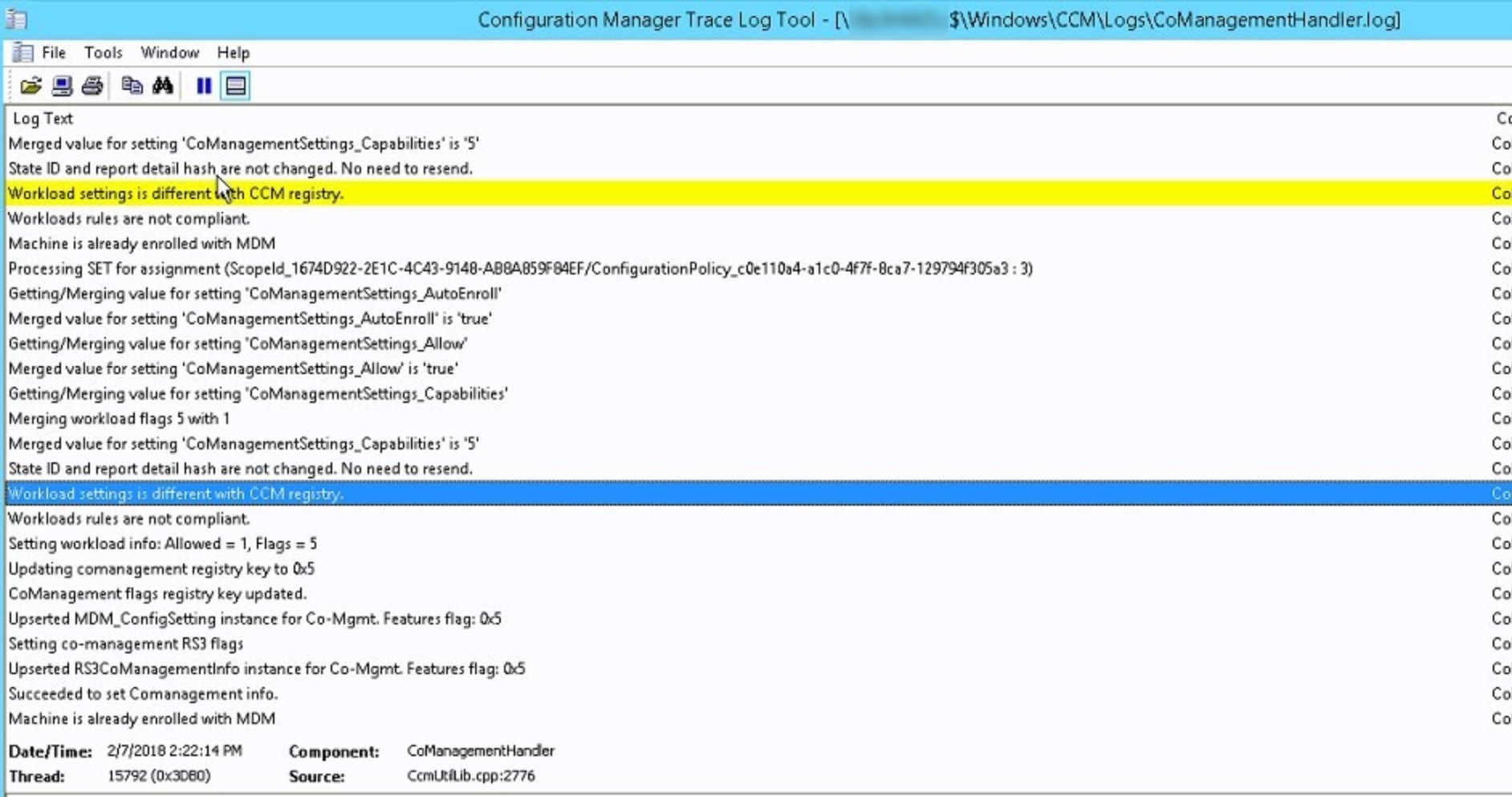
- On the client, the CoManagementHandler.log will provide the details.
- Note that during our testing, this took a while to get going in the logs. Many errors show up before it works correctly, without changing a thing. Patience is key.
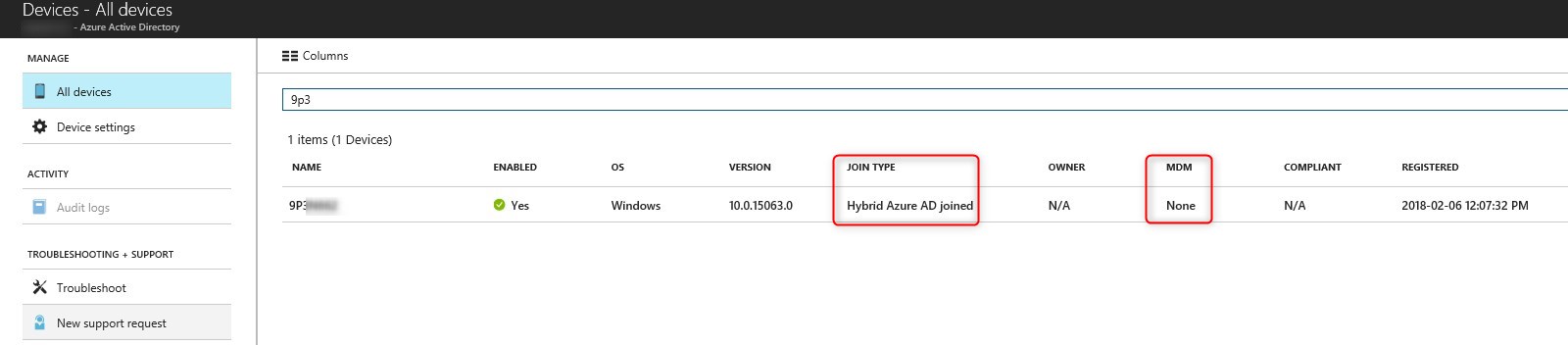
After a little while (hours) the client will change from MDM – none to MDM – Intune
Before MDM managed
 After MDM managed
After MDM managed
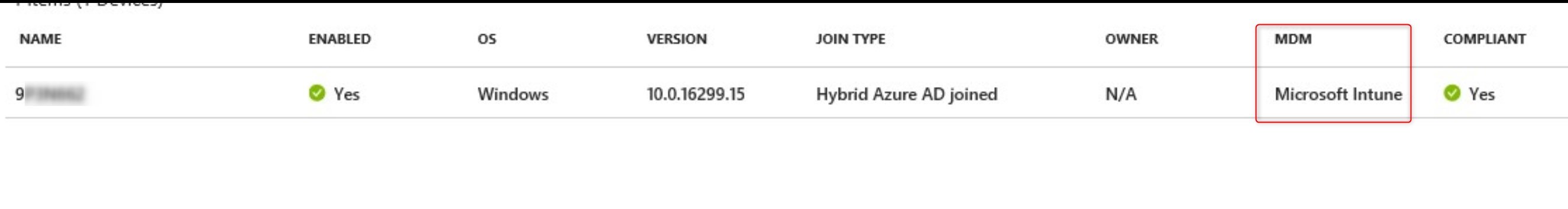 It will eventually report that the device is managed by MDM/ConfigMgr Agent
It will eventually report that the device is managed by MDM/ConfigMgr Agent
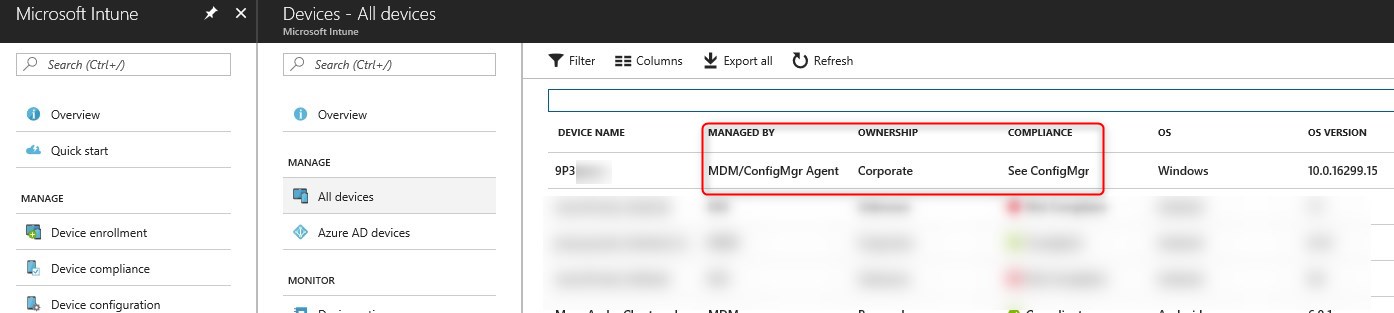
At that point, it’s time to configure Intune policy to eventually switch Workloads
More details about switching workload to Intune on Microsoft learn.
SCCM Comanagement Monitoring
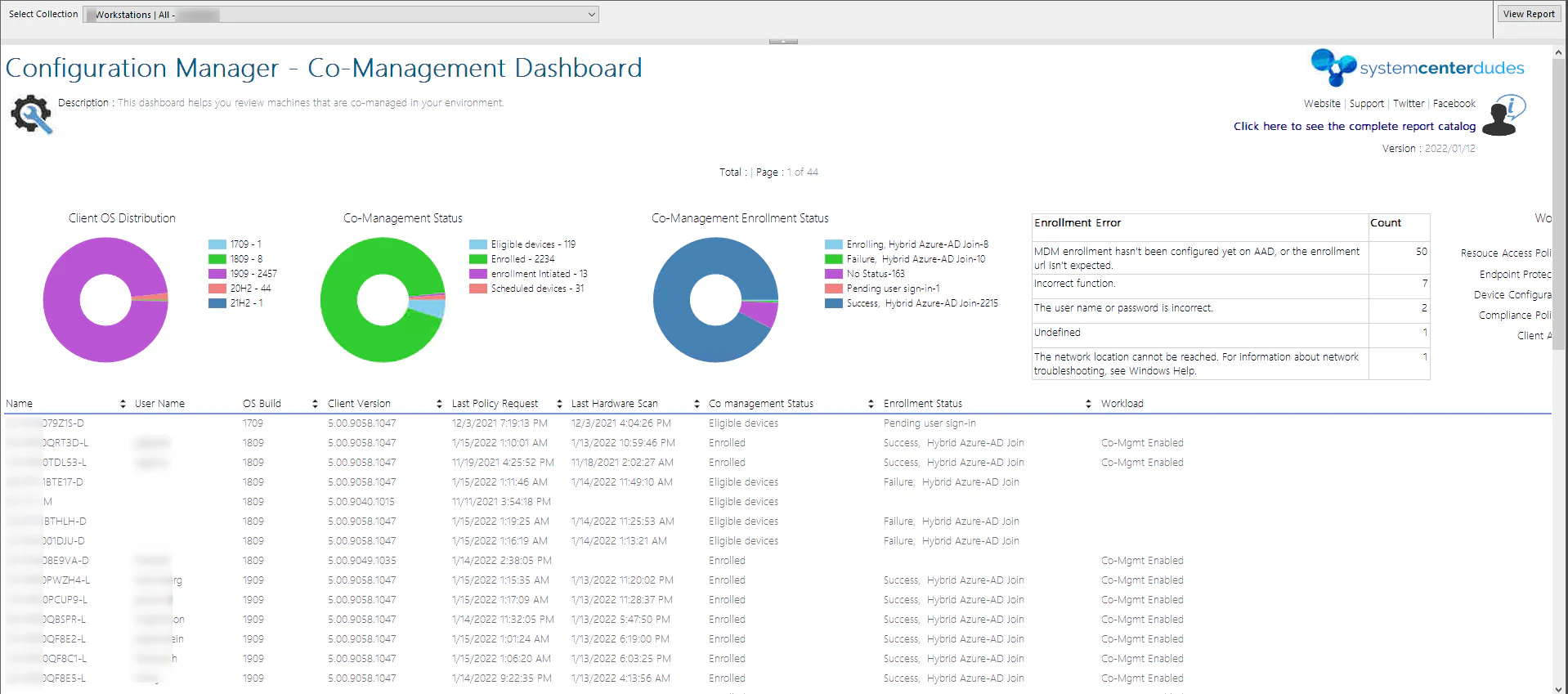
To monitor your SCCM Comanament Clients, you can use the console or use our CoManagement Dashboard.















Suraj Malusare
04.17.2019 AT 12:38 AMDayanand
10.24.2018 AT 04:43 AMGatis
10.01.2018 AT 04:42 AMAnubhav Sharma
07.22.2018 AT 12:04 PMJan
06.20.2018 AT 04:24 AMJohn
04.23.2018 AT 09:43 AMRkast
04.19.2018 AT 03:22 PMJames
04.18.2018 AT 10:43 AMRkast
03.20.2018 AT 01:09 PMJonathan Lefebvre
03.21.2018 AT 10:37 AMlvillesystemsjockey
10.25.2018 AT 10:00 AM